Importance of Hydration for Athletes
Hydration is a critical aspect of an athlete’s sports nutrition game plan. Dehydration can negatively impact an athlete’s health as well as sports performance.
Let’s take a look at the importance of hydration for athletes. Then we will explore strategies for supporting athletes with meeting their hydration needs during activity.
Importance of Hydration for Athletes: Health
Water is an essential nutrient that is required for life. It has many important roles in the body, including transporting nutrients to cells, serving as a solvent, lubricant, and shock absorber, and helping regulate body temperature (1).
The body precisely regulates water balance to ensure optimal function of all of the body’s systems (1). Even mild dehydration (>1%) compromises the body’s ability to regulate internal body temperature. As dehydration becomes more severe, the risk of an athlete developing a heat illness increases (2).
In addition to heat illnesses, dehydration increases the stress on the cardiovascular system during exercise. As an athlete becomes progressively dehydrated, the following occurs (2):
- Decrease in the amount of blood pumped by the heart per beat (stroke volume)
- Increased heart rate
- Increased vascular resistance
- Decreased cardiac output
For these reasons, it is important for athletes to make hydration a daily priority. In addition, athletes should have a hydration plan in place for both practices and competition.
Warning Signs of Dehydration
It is important for athletes to be aware of the warning signs of dehydration. By recognizing the early signs and symptoms of dehydration, athletes can take action and prevent the development of heat illnesses.
Warning signs of dehydration include (2):
- Thirst
- Fatigue
- Flushed skin
- Feelings of discomfort
- Headaches, dizziness, lightheadedness
- GI cramping, diarrhea
- Nausea, vomiting
- Chills or heat sensations
- Decreased performance
As discussed above, dehydration increases the risk of an athlete developing a heat illness, especially when exercising in a hot and humid environment (3).
Warning Signs of Heat Illness
Exertional heat illnesses, including heat exhaustion and heat stroke, occur during physical activity (4). Coaches, athletic trainers, parents, and athletes should all be aware of the signs and symptoms of exertional heat illnesses. Heat stroke can result in severe medical concerns, including organ damage, and it can be fatal (5).
Signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion and heat illness are listed in the table below (4).
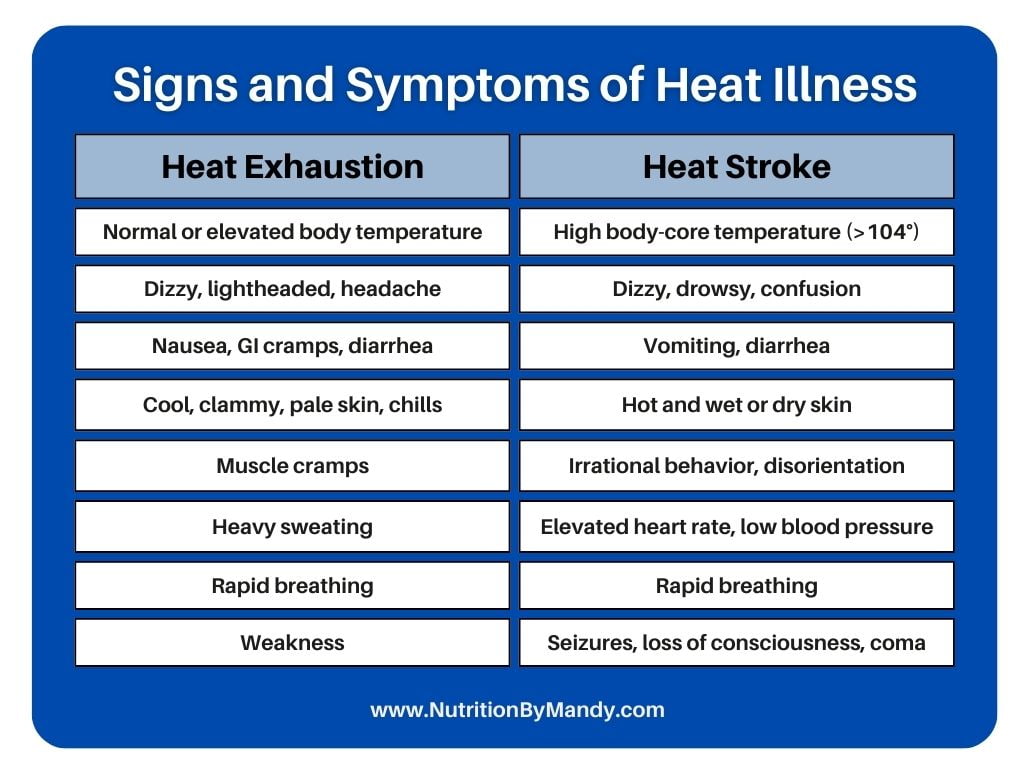
If an athlete is exhibiting signs of heat exhaustion or heat stroke, it is imperative the athlete stop exercising and receive immediate medical treatment. Exertional heat stroke is associated with organ damage and can result in death (4, 5).
Importance of Hydration for Athletes: Sports Performance
In addition to health, hydration is important for supporting an athlete’s sports performance. Even mild dehydration can negatively impact cognitive function and aerobic sports performance (3).
In addition to aerobic performance, strength, power, and muscle endurance are also impaired by dehydration of greater than 2% of body weight (2, 6). Dehydration also increases an athlete’s feelings of perceived exertion during exercise. As dehydration becomes more severe, further decreases in performance are seen (3).
However, despite the importance of hydration for health and performance, the majority of athletes begin their workouts in a dehydrated state (2).
Daily Hydration Strategies for Athletes
Given the importance of hydration for health and performance, athletes should make hydration a daily priority. Consuming fluid with each meal and snack can help athletes with meeting their daily hydration needs.
In addition, athletes can enjoy fruits and vegetables that contain a high-water content as part of their sports nutrition diet. Foods such as watermelon, cantaloupe, oranges, strawberries, celery, and cucumbers all have a high-water content and make a great addition to an athlete’s meal plan.
Athletes should also consider carrying a refillable water bottle with them throughout the day. This can help serve as a reminder to athletes to consume fluid during the day to support their hydration needs.

Hydration Needs of Athletes
When athletes sweat, they lose both fluids and electrolytes. The main electrolyte lost in sweat is sodium. Therefore, when considering hydration needs of athletes, it is important to consider both fluids and electrolytes.
Importance of Hydration for Athletes: Individualized Hydration Plan
Athletes vary greatly in regard to the amount of fluid and electrolytes they lose in sweat. The sweat rates of adults during exercise have been found to range from 0.5 to 4.0 L/hour. While the amount of sodium lost in sweat during exercise ranges between 0.2 and 7.3 g/hour (2).
The Gatorade Sports Science Institute has a Fluid Loss Calculator available on their website. Athletes can use this tool to help them estimate their hourly sweat rate during exercise.
It should be noted that an athlete’s sweat rate can also vary depending upon a variety of factors including (2):
- Exercise intensity
- Type of exercise
- Athlete’s body size
- Uniform or clothing worn
- Environmental conditions (temperature, humidity)
- Acclimatization of the athlete to the environment
Thus, when calculating sweat rate for competition, athletes should do so in an environment as close to the actual competition as possible.
Given the variability in fluid and electrolytes lost in sweat amongst athletes, it can be beneficial for athletes to work with a sports dietitian nutritionist to develop an individualized hydration plan for activity.

Hydration Strategies for Athletes Before, During, and After Activity
It is important for athletes to have a hydration plan in place for hydrating before, during, and following activity (2). Although athletes’ individual hydration needs vary; below are some general hydration tips for athletes surrounding activity.
Hydration Before Activity
Athletes should aim to start the workout or competition in an optimally hydrated state. Approximately 4 hours prior to the activity, athletes should aim to drink 5-7 mL of fluid per kg of body weight (3).
For a 165-pound athlete, this calculates to be ~13 – 18 fl oz. In general, athletes can aim to drink ~16 fl oz (2 cups) of fluid with their pregame meal ~4 hours prior to the event.
Athletes can continue hydrating with water or a sports drink in the hour leading up to the competition, drinking approximately 8 oz of fluid during this time period.
Hydration During Activity
As previously discussed, hydration needs vary greatly for athletes. However, a general guide is that athletes aim to drink ~3-8 ounces of fluid every 15-20 minutes (0.4-0.8 L per hour) of activity (3, 7).
Drinking a big gulp of water or sports drink is equivalent to approximately 1 ounce of fluid. Thus, athletes can aim for several big gulps from their water bottle every 15-20 minutes of activity or as competition allows.
Hydration Following Activity
Following activity, rehydrating should be an important part of an athlete’s recovery nutrition game plan. Athletes should be mindful of replacing both the fluid and the electrolytes lost in sweat.
Weighing before and after activity can help athletes determine how much fluid was lost in sweat. For each pound of weight lost during the activity, athletes should aim to drink 20-24 oz of fluid (7).
Consuming sodium, in either food or beverages, following activity can help athletes with replacing the sodium lost in sweat. In addition, sodium helps athletes to better retain the fluid consumed after exercise (3).

Importance of Rehydrating Following Activity
Rehydrating with fluids and electrolytes is particularly important for athletes when they are doing multiple workouts within the same day or repeated days of hard training. When athletes do not replace the fluid lost during an exercise session, they will start the next workout or competition in a dehydrated state (3).
Cumulative dehydration over several days can increase an athlete’s risk of developing a heat illness and negatively impact sports performance (4).
One final reminder to athletes regarding rehydrating following activity: Although it feels good on a hot day to pour the water over your head, to hydrate the body, athletes must actually drink the water.
Importance of Hydration for Athletes
You now have an overview of the importance of hydration for athletes. Coaches, athletic trainers, and parents can help reinforce the need for athletes to make hydration a daily priority to support their health and performance.
For additional sports nutrition tips for athletes, check out my blog on healthy snacks for athletes to support performance.
Join the Nutrition By Mandy Email List & Get a Free Athlete’s Grocery List
Click HERE to join the Nutrition By Mandy e-mail list. When you join you will receive a free athlete’s grocery list to print and take with you to the store.
About Mandy
Mandy is a Sports Dietitian Nutritionist in the San Antonio, TX area. She is a Registered and Licensed Dietitian, a Board-Certified Specialist in Sports Dietetics, a Licensed Athletic Trainer, and is a Certified Exercise Physiologist through the American College of Sports Medicine. Mandy has experience working with athletes at the high school, collegiate, and professional levels. She believes the key to reaching one’s full potential, both in everyday life and in sports performance, relies on a healthy nutritional foundation. Learn more about the work Mandy does here.


Pingback: 10 Whataburger Healthy Options for Athletes - Nutrition By Mandy